Objective: The objectives of this study are to analyze the association between anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA) and cardiac involvement in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) and to evaluate the diagnostic value of AMA for cardiac involvement in IIM patients.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search in PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library to identify English-language studies published before November 19, 2021. Stata 12.0 software (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA) was used for the statistical analyses. We used the sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve to evaluate the diagnostic value of AMA for cardiac involvement in IIM patients. Statistical heterogeneity of studies was assessed using the I2 statistic with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
Results: Seven studies were included in the final analyses, with a total of 2308 IIM patients (including 171 AMA-positive and 2137 AMA-negative patients). The pooled sensitivity of AMA for cardiac involvement in IIM patients was 0.29 (95% CI: 0.19-0.43) and specificity was 0.92 (95% CI: 0.88-0.96). The pooled PLR was 3.9 (95% CI: 2.82-5.38), NLR was 0.76 (95% CI: 0.66-0.88), and the diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) was 5 (95% CI: 3-7). The area under the SROC curve was 0.76 (95% CI: 0.72-0.79).
Conclusion: The overall diagnostic value of AMA may not be very high for cardiac involvement in IIM patients.
In this paper, we consider reaction-diffusion epidemic models with mass action or standard incidence mechanism and study the impact of limiting population movement on disease transmissions. We set either the dispersal rate of the susceptible or infected people to zero and study the corresponding degenerate reaction-diffusion model. Our main approach to study the global dynamics of these models is to construct delicate Lyapunov functions. Our results show that the consequences of limiting the movement of susceptible or infected people depend on transmission mechanisms, model parameters and population size.
This article is devoted to the analysis of the parabolic–parabolic chemotaxis system with multi-components over 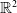 $mathbb{R}^2$. The optimal small initial condition on the global existence of solutions for multi-species chemotaxis model in the fully parabolic situation had not been attained as far as the author knows. In this paper, we prove that under the sub-critical mass condition, any solutions to conflict-free system exist globally. Moreover, the global existence of solutions to system with strong self-repelling effect has been discussed even for large initial data. The proof is based on the modified free energy functional and the Moser–Trudinger inequality for system.
$mathbb{R}^2$. The optimal small initial condition on the global existence of solutions for multi-species chemotaxis model in the fully parabolic situation had not been attained as far as the author knows. In this paper, we prove that under the sub-critical mass condition, any solutions to conflict-free system exist globally. Moreover, the global existence of solutions to system with strong self-repelling effect has been discussed even for large initial data. The proof is based on the modified free energy functional and the Moser–Trudinger inequality for system.

