Loss functions with a large number of saddle points are one of the major obstacles for training modern machine learning (ML) models efficiently. First-order methods such as gradient descent (GD) are usually the methods of choice for training ML models. However, these methods converge to saddle points for certain choices of initial guesses. In this paper, we propose a modification of the recently proposed Laplacian smoothing gradient descent (LSGD) [Osher et al., arXiv:1806.06317], called modified LSGD (mLSGD), and demonstrate its potential to avoid saddle points without sacrificing the convergence rate. Our analysis is based on the attraction region, formed by all starting points for which the considered numerical scheme converges to a saddle point. We investigate the attraction region’s dimension both analytically and numerically. For a canonical class of quadratic functions, we show that the dimension of the attraction region for mLSGD is ��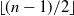 ��$lfloor (n-1)/2rfloor$���, and hence it is significantly smaller than that of GD whose dimension is ��
��$lfloor (n-1)/2rfloor$���, and hence it is significantly smaller than that of GD whose dimension is ��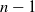 ��$n-1$���.
��$n-1$���.
Loss functions with a large number of saddle points are one of the major obstacles for training modern machine learning (ML) models efficiently. First-order methods such as gradient descent (GD) are usually the methods of choice for training ML models. However, these methods converge to saddle points for certain choices of initial guesses. In this paper, we propose a modification of the recently proposed Laplacian smoothing gradient descent (LSGD) [Osher et al., arXiv:1806.06317], called modified LSGD (mLSGD), and demonstrate its potential to avoid saddle points without sacrificing the convergence rate. Our analysis is based on the attraction region, formed by all starting points for which the considered numerical scheme converges to a saddle point. We investigate the attraction region’s dimension both analytically and numerically. For a canonical class of quadratic functions, we show that the dimension of the attraction region for mLSGD is ��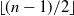 ��$lfloor (n-1)/2rfloor$���, and hence it is significantly smaller than that of GD whose dimension is ��
��$lfloor (n-1)/2rfloor$���, and hence it is significantly smaller than that of GD whose dimension is ��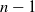 ��$n-1$���.
��$n-1$���.

